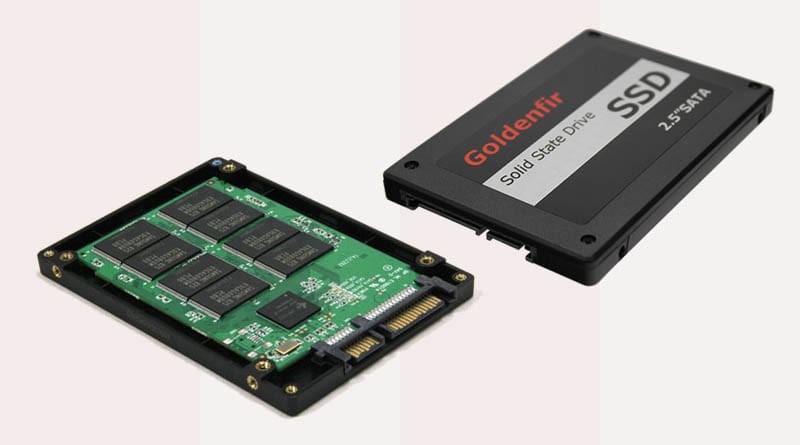
SSD (Solid State Drive)
$59.00
A Solid State Drive (SSD) is a modern storage device that uses flash memory to deliver lightning-fast speed, improved durability, and energy efficiency compared to traditional hard drives.
In today’s digital world, where speed and efficiency matter more than ever, the Solid State Drive (SSD) has emerged as one of the most important technological advancements in the storage industry. Whether you are using a laptop, desktop, gaming console, or enterprise server, SSDs are becoming the standard for storing and accessing data. Unlike the traditional Hard Disk Drive (HDD), which uses spinning magnetic disks to read and write data, an SSD relies on NAND flash memory chips, eliminating moving parts and resulting in faster performance, better reliability, and lower energy consumption.
This detailed guide will explore what SSDs are, how they work, their advantages, different types, applications, and future trends.
What is an SSD?
A Solid State Drive (SSD) is a type of storage device that stores data on flash memory chips rather than mechanical platters. The word “solid state” refers to the fact that it has no moving parts, making it faster and more durable than older technologies.
SSDs are commonly used in personal computers, gaming consoles, tablets, smartphones, and high-performance servers. The widespread adoption of SSDs is driven by the demand for quick boot times, fast file transfers, and seamless multitasking.
How Does an SSD Work?
At the core of every SSD are NAND flash memory chips that hold data permanently, even when the power is turned off. The controller, a built-in processor, manages where data is stored and retrieved, optimizing speed and performance.
Here’s a simple breakdown of how SSDs work:
Data Storage: Files and applications are stored as electrical charges within NAND cells.
Data Access: When you open a file, the controller fetches the data almost instantly, unlike an HDD that requires the disk to spin.
Wear Leveling: The controller spreads out data evenly across memory cells to prolong lifespan.
Cache and DRAM: Some SSDs use additional cache memory to further speed up read and write operations.
Types of SSDs
SATA SSDs
The most common and affordable type.
Uses the same interface as traditional hard drives.
Speeds are limited (around 500–600 MB/s).
NVMe SSDs (PCIe)
Connect directly to the motherboard via PCI Express lanes.
Extremely fast, reaching speeds up to 7,000 MB/s or more.
Ideal for gamers, content creators, and professionals.
M.2 SSDs
A form factor, not a speed standard.
Can use either SATA or NVMe protocols.
Compact and perfect for ultrabooks and slim devices.
U.2 SSDs
Mainly used in enterprise environments.
High durability and consistent performance.
External SSDs
Portable drives connected via USB or Thunderbolt.
Popular for backups and data transfers.
Advantages of SSDs
Blazing Speed
SSDs can boot an operating system within seconds and transfer large files at lightning-fast speeds.
Applications load instantly, improving productivity.
Durability
No moving parts, making them less prone to damage from drops, shocks, or vibrations.
Energy Efficiency
Consumes less power compared to HDDs, improving laptop battery life.
Silent Operation
SSDs operate silently, unlike HDDs, which produce noise due to spinning disks.
Compact Size
Available in slim designs like M.2, making them ideal for lightweight laptops and tablets.
Longer Lifespan
With wear-leveling technology, modern SSDs can last many years under normal use.
SSD vs. HDD – A Comparison
Feature HDD (Hard Disk Drive) SSD (Solid State Drive)
Speed 50–150 MB/s 500–7,000+ MB/s
Durability Prone to damage (moving parts) Highly durable (no moving parts)
Noise Audible spinning and clicks Completely silent
Power Consumption Higher Lower (better for laptops)
Price per GB Cheaper More expensive (but dropping)
Boot Time 30–60 seconds 5–10 seconds
Applications of SSDs
Personal Computers & Laptops
Faster startup, smooth multitasking, and longer battery life.
Gaming
Reduced game loading times and smoother gameplay.
Content Creation
Ideal for video editing, 3D rendering, and graphic design.
Enterprise Servers
Handles huge data loads with low latency, essential for cloud computing and databases.
Portable Storage
External SSDs are lightweight, shockproof, and faster than USB flash drives.
Challenges of SSDs
Cost: SSDs are still more expensive than HDDs in terms of cost per gigabyte.
Limited Write Cycles: NAND flash memory has a finite number of write operations, although modern SSDs last for years under normal usage.
Data Recovery: If an SSD fails, data recovery is harder compared to HDDs.
Future of SSDs
The future of SSD technology looks promising, with innovations like:
Higher Storage Capacities – SSDs exceeding 10TB for consumers.
Faster NVMe Standards – PCIe Gen 5.0 SSDs already crossing 13,000 MB/s.
Better Affordability – Prices are dropping rapidly as NAND manufacturing improves.
Hybrid Storage Solutions – Combining SSD speed with HDD capacity.
AI-Powered Storage Management – Smart controllers optimizing performance automatically.
Conclusion
The Solid State Drive (SSD) is no longer a luxury but a necessity in today’s fast-paced digital lifestyle. With unmatched speed, reliability, and energy efficiency, SSDs have transformed how we store and access data. From personal laptops to enterprise-level servers, SSDs are the backbone of modern computing.
Although slightly more expensive than HDDs, the benefits of speed, durability, and performance outweigh the cost for most users. As technology continues to evolve, SSDs will become even faster, cheaper, and more widely adopted, making them the ultimate solution for the future of storage.


MAECENAS IACULIS
Vestibulum curae torquent diam diam commodo parturient penatibus nunc dui adipiscing convallis bulum parturient suspendisse parturient a.Parturient in parturient scelerisque nibh lectus quam a natoque adipiscing a vestibulum hendrerit et pharetra fames nunc natoque dui.
ADIPISCING CONVALLIS BULUM
- Vestibulum penatibus nunc dui adipiscing convallis bulum parturient suspendisse.
- Abitur parturient praesent lectus quam a natoque adipiscing a vestibulum hendre.
- Diam parturient dictumst parturient scelerisque nibh lectus.
Scelerisque adipiscing bibendum sem vestibulum et in a a a purus lectus faucibus lobortis tincidunt purus lectus nisl class eros.Condimentum a et ullamcorper dictumst mus et tristique elementum nam inceptos hac parturient scelerisque vestibulum amet elit ut volutpat.










Reviews
There are no reviews yet.